Summary
Wikipedia annotation Edit Wikipedia article
The Rfam group coordinates the annotation of Rfam families in Wikipedia. This family is described by a Wikipedia entry Mir-351 microRNA precursor family. More...
This page is based on a Wikipedia article. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.
Sequences
Quick actions
Table view (5 sequence regions)
| Original order | Download FASTA | Accession | Bit score | Type | Start | End | Description | Species | View context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | URS000075C074_10116 | N/A | seed | 9 | 81 | Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) microRNA rno-mir-351 precursor (rno-mir-351-1, rno-mir-351-2) | Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) | ||
| 1 | URS000062BA5C_10090 | N/A | seed | 9 | 83 | Mus musculus (house mouse) microRNA mmu-mir-351 precursor | Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||
| 0 | CM001013.3 | 106.90 | full | 52,142,222 | 52,142,148 | CM001013.3 Mus musculus chromosome X, GRCm39 reference primary assembly C57BL/6J | Mus musculus (house mouse) |
|
|
| 1 | CM026994.1 | 103.00 | full | 132,805,635 | 132,805,563 | CM026994.1 Rattus norvegicus strain BN/NHsdMcwi chromosome X, whole genome shotgun sequence | Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
|
|
| 2 | QGOO02000035.1 | 102.20 | full | 727,438 | 727,511 | QGOO02000035.1 Mus spicilegus strain ZRU musp714_scaffold_00035b, whole genome shotgun sequence | Mus spicilegus (steppe mouse) |
|
Alignment
There are various ways to view or download the seed alignments that we store. You can use a sequence viewer to look at them, or you can look at a plain text version of the sequence in a variety of different formats. More...
View options
You can view Rfam seed alignments in your browser in various ways. Choose the viewer that you want to use and click the "View" button to show the alignment in a pop-up window.
Formatting options
You can view or download Rfam seed alignments in several formats. Check either the "download" button, to save the formatted alignment, or "view", to see it in your browser window, and click "Generate".
Download
Download a gzip-compressed, Stockholm-format file containing the seed alignment for this family. You may find RALEE useful when viewing sequence alignments.
Submit a new alignment
We're happy receive updated seed alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
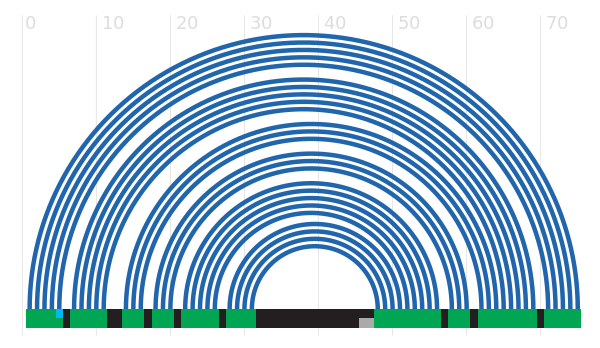
Secondary structure
This section shows a variety of different secondary structure representations for this family. More...
You can view the secondary structure of the family using the VARNA applet. You can see more information about VARNA iself here.
Current Rfam structure
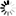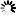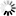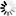 Loading...
Loading...
R-scape optimised structure
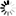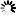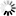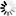 Loading...
Loading...
- Colours
- Statistically significant basepair with covariation
- 97% conserved nucleotide
- 90% conserved nucleotide
- 75% conserved nucleotide
- 50% conserved nucleotide
- Nucleotides
- R: A or G
- Y: C or U
Tip: The diagrams are interactive:
you can pan and zoom to see more details
or hover over nucleotides and basepairs.
R-scape is a method for testing whether covariation analysis supports the presence of a conserved RNA secondary structure. This page shows R-scape analysis of the secondary structure from the Rfam seed alignment and a new structure with covariation support that is compatible with the same alignment.
To find out more about the method, see the R-scape paper by Rivas et al., 2016. The structures are visualised using R2R.
Species distribution
Sunburst controls
HideLineage
Move your mouse over the main tree to show the lineage of a particular node.
You can move this pane by dragging it.
Weight segments by...
Change the size of the sunburst
Colour assignments
 Archea
Archea
|
 Eukaryota
Eukaryota
|
 Bacteria
Bacteria
|
 Other sequences
Other sequences
|
 Viruses
Viruses
|
 Unclassified
Unclassified
|
 Viroids
Viroids
|
 Unclassified sequence
Unclassified sequence
|
Selections
Click on a node to select that node and its sub-tree.
Clear selection
This visualisation provides a simple graphical representation of the distribution of this family across species. You can find the original interactive tree in the adjacent tab. More...
Tree controls
HideThe tree shows the occurrence of this RNA across different species. More...
Loading...
Please note: for large trees this can take some time. While the tree is loading, you can safely switch away from this tab but if you browse away from the family page entirely, the tree will not be loaded.
Trees
This page displays the predicted phylogenetic tree for the alignment. More...
Note: You can also download the data file for the seed tree.
References
This section shows the database cross-references that we have for this Rfam family.
Literature references
-
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M, Lin C, Socci ND, Hermida L, Fulci V, Chiaretti S, Foa R, Schliwka J, Fuchs U, Novosel A, Muller RU, Schermer B, Bissels U, Inman J, Phan Q, Chien M, Weir DB, Choksi R, De Vita G, Frezzetti D, Trompeter HI, Hornung V, Teng G, Hartmann G, Palkovits M, Di Lauro R, Wernet P, Macino G, Rogler CE, Nagle JW, Ju J, Papavasiliou FN, Benzing T, Lichter P, Tam W, Brownstein MJ, Bosio A, Borkhardt A, Russo JJ, Sander C, Zavolan M, Tuschl T; Cell. 2007;129:1401-1414. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. PUBMED:17604727
-
Ahn HW, Morin RD, Zhao H, Harris RA, Coarfa C, Chen ZJ, Milosavljevic A, Marra MA, Rajkovic A Mol Hum Reprod. 2010;16:463-471. MicroRNA transcriptome in the newborn mouse ovaries determined by massive parallel sequencing PUBMED:20215419
-
Zhu JY, Strehle M, Frohn A, Kremmer E, Hofig KP, Meister G, Adler H J Virol. 2010;1:1. Identification and analysis of expression of novel microRNAs of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 PUBMED:20668074
-
Chiang HR, Schoenfeld LW, Ruby JG, Auyeung VC, Spies N, Baek D, Johnston WK, Russ C, Luo S, Babiarz JE, Blelloch R, Schroth GP, Nusbaum C, Bartel DP Genes Dev. 2010;24:992-1009. Mammalian microRNAs: experimental evaluation of novel and previously annotated genes PUBMED:20413612
-
Kim J, Krichevsky A, Grad Y, Hayes GD, Kosik KS, Church GM, Ruvkun G Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004;101:360-365. Identification of many microRNAs that copurify with polyribosomes in mammalian neurons. PUBMED:14691248
-
Watanabe T, Takeda A, Tsukiyama T, Mise K, Okuno T, Sasaki H, Minami N, Imai H Genes Dev. 2006;20:1732-1743. Identification and characterization of two novel classes of small RNAs in the mouse germline: retrotransposon-derived siRNAs in oocytes and germline small RNAs in testes. PUBMED:16766679
-
Linsen SE, de Wit E, de Bruijn E, Cuppen E; BMC Genomics. 2010;11:249. Small RNA expression and strain specificity in the rat. PUBMED:20403161
-
Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D155. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. PUBMED:30423142
External database links
| Gene Ontology: | GO:0016442 (RISC complex); GO:0035195 (miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing); |
| Sequence Ontology: | SO:0001244 (pre_miRNA); |
| MIPF: | MIPF0000244 |
Curation and family details
This section shows the detailed information about the Rfam family. We're happy to receive updated or improved alignments for new or existing families. Submit your new alignment and we'll take a look.
Curation
| Seed source | Griffiths-Jones SR | ||||||
| Structure source | Predicted; RNAalifold | ||||||
| Type | Gene; miRNA; | ||||||
| Author |
Griffiths-Jones SR
|
||||||
| Alignment details |
|
Model information
| Build commands |
cmbuild -F CM SEED
cmcalibrate --mpi CM
|
| Search command |
cmsearch --cpu 4 --verbose --nohmmonly -T 25.00 -Z 2958934 CM SEQDB
|
| Gathering cutoff | 70.0 |
| Trusted cutoff | 102.2 |
| Noise cutoff | 59.8 |
| Covariance model | Download |